相关信息
Vectors are directions. A vector has a direction and a magnitude (also known as its strength or length).
如果向量的属性既带有direction 又 带有 magnitude,那么它就不只是direction,而是在指定方向上移动的距离。
效果 实现
效果
|400x357 实现
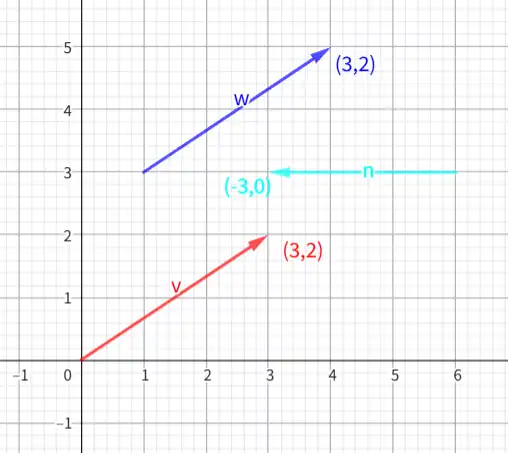
w=Vector((1,3),(4,5)) n=Vector((6,3),(3,3)) v=Vector((3,2)) 相关信息
Since vectors represent directions, the origin of the vector does not change its value.
向量的值仅和其指向以及长度有关,上图中 w ⃗ \vec{w} w v ⃗ \vec{v} v
关于指向:上图中的文本(3,2)表示向x轴正方向移动3个单位长度,向y轴正方向移动2个单位长度。
由于vector 只表示指向,可以有无数个vector表示同一指向。为了具体地描述向量,选择起点为原点的向量代表该指向。原点作为默认起点,此时向量的终点就可以表示该向量。
v ⃗ = ( x y z ) \vec{v}=\begin{pmatrix}x\\y\\z\end{pmatrix} v = x y z
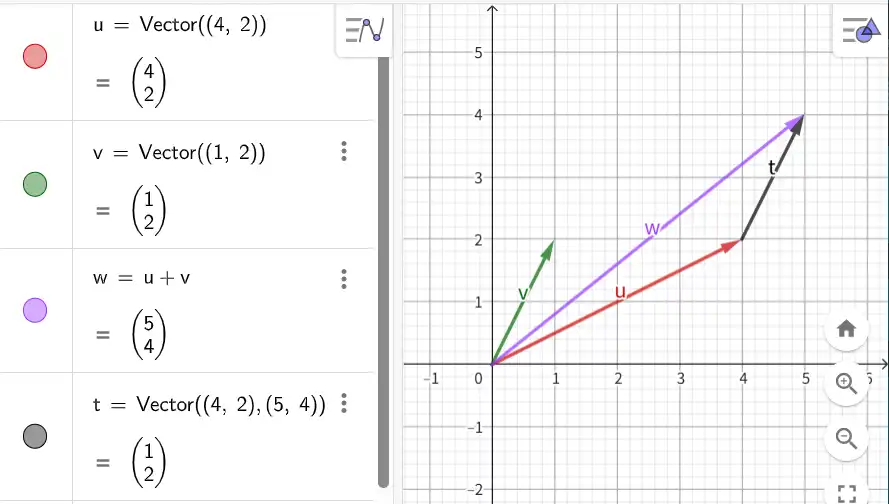
|500x283 t ⃗ \vec{t} t v ⃗ \vec{v} v
相关信息
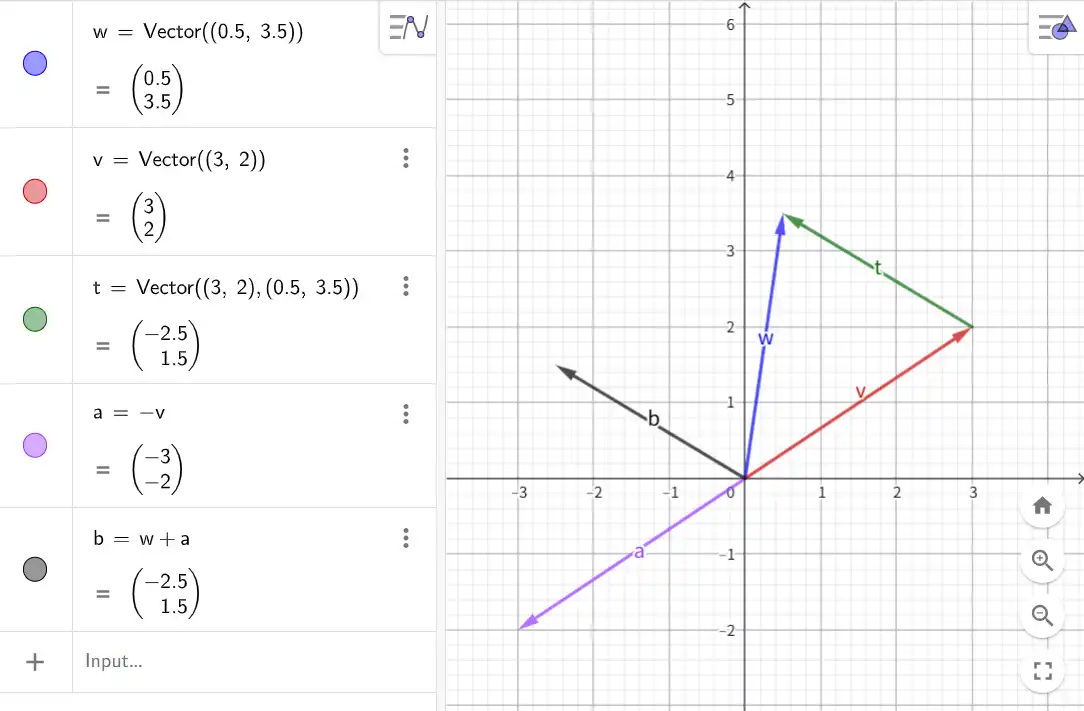
Negating a vector results in a vector in the reversed direction.
− v ⃗ = − ( v x v y v z ) = ( − v x − v y − v z ) -\vec{v} = -\begin{pmatrix} v_x \\ v_y \\ v_z \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} -v_x \\ -v_y \\ - v_z \end{pmatrix} − v = − v x v y v z = − v x − v y − v z
|498x327 先按照第一个向量的方向前进,然后按照第二个向量的相反向量前进。
w ⃗ − v ⃗ = w ⃗ + − v ⃗ \vec{w} - \vec{v} = \vec{w} + - \vec{v} w − v = w + − v
减去一个向量相当于和它的相反向量相加
( 1 2 3 ) + x → ( 1 2 3 ) + ( x x x ) + = ( 1 + x 2 + x 3 + x ) \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} + x \to \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} x \\ x \\ x \end{pmatrix} + = \begin{pmatrix} 1 + x \\ 2 + x \\ 3 + x \end{pmatrix} 1 2 3 + x → 1 2 3 + x x x + = 1 + x 2 + x 3 + x
每个方向上进行放大或缩小
|296x180 ∣ ∣ v ⃗ ∣ ∣ = x 2 + y 2 ||\vec{v}|| = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2} ∣∣ v ∣∣ = x 2 + y 2
unit vector unit vector
n ^ = v ⃗ ∣ ∣ v ∣ ∣ \hat{n} = { \vec{v} \over | |v| | } n ^ = ∣∣ v ∣∣ v
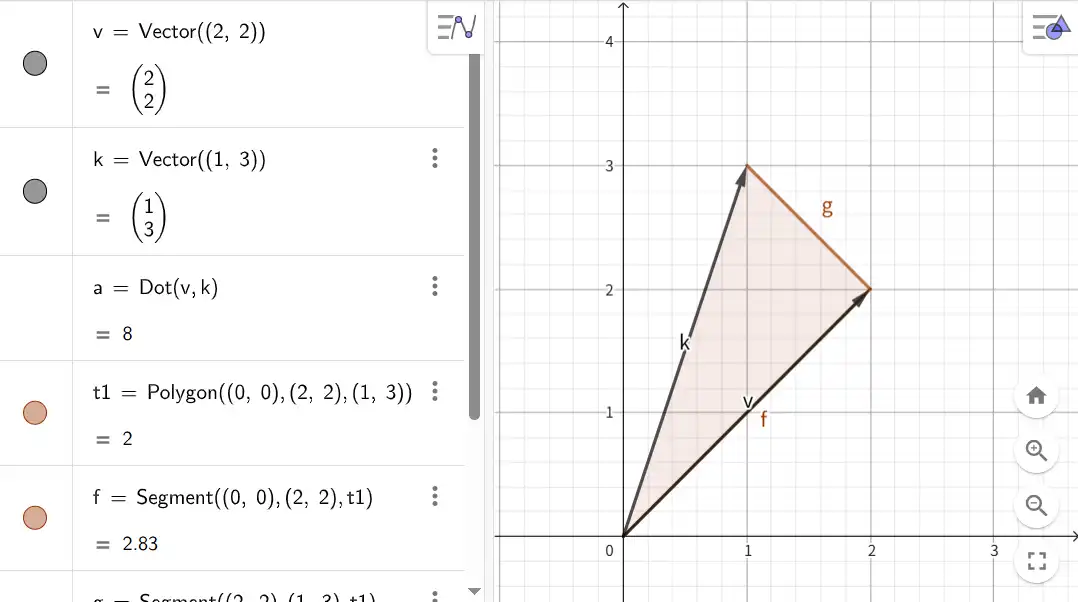
v ⃗ ⋅ k ⃗ = ∣ ∣ v ⃗ ∣ ∣ ⋅ ∣ ∣ k ⃗ ∣ ∣ ⋅ cos θ \vec{v} \cdot \vec{k} = ||\vec{v}|| \cdot ||\vec{k}|| \cdot \cos\theta v ⋅ k = ∣∣ v ∣∣ ⋅ ∣∣ k ∣∣ ⋅ cos θ
其中θ 为两个向量的夹角这个角度值的定义?
公式的几何含义:一个向量在另一个向量上的投影长度 乘以 另一个向量的长度
作用 v ⃗ \vec{v} v k ⃗ \vec{k} k cos θ \cos\theta cos θ
计算
( 2 2 ) ⋅ ( 1 3 ) = ( 2 ∗ 1 ) + ( 2 ∗ 3 ) = 8 \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 2 \end{pmatrix} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} = (2 * 1) + (2 * 3) = 8 ( 2 2 ) ⋅ ( 1 3 ) = ( 2 ∗ 1 ) + ( 2 ∗ 3 ) = 8
v ⃗ \vec{v} v v ⃗ \vec{v} v k ⃗ \vec{k} k v ⃗ \vec{v} v v ⃗ \vec{v} v 2 2 2\sqrt{2} 2 2
相关信息
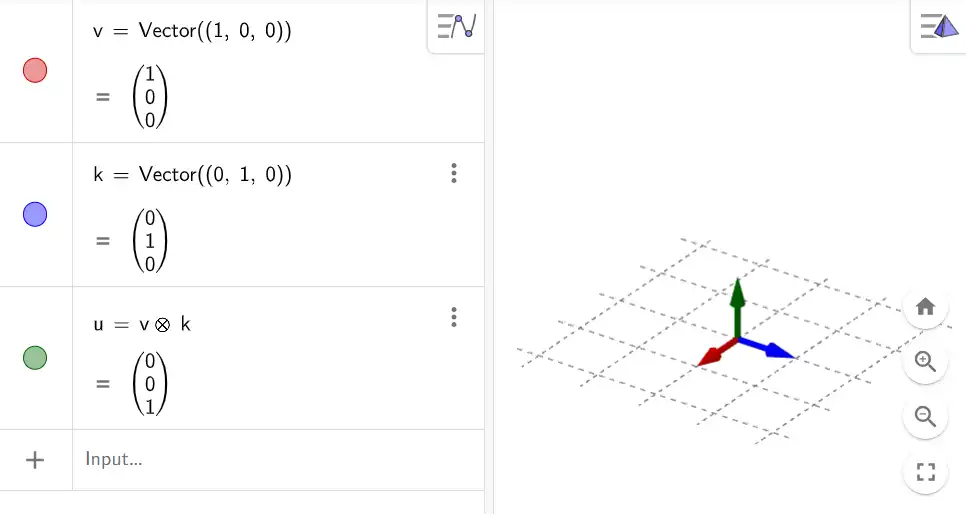
The cross product takes two non-parallel vectors as input and produces a third vector that is orthogonal to both the input vectors.
二维向量叉积的结果是:
a × b = ∣ a ∣ ∣ b ∣ sin θ a \times b = |a||b|\sin \theta a × b = ∣ a ∣∣ b ∣ sin θ
θ:从a逆时针旋转到b的角度
三维向量中,对于两个不平行的两个向量,其叉积结果是生成一个垂直于两个输入向量(平面)的向量。
计算
( A x A y A z ) × ( B x B y B z ) = ( A y B z − A z B y A z B x − A x B z A x B y − A y B x ) \begin{pmatrix} \color{red} A_x \\ \color{green} A_y \\ \color{blue} A_z \end{pmatrix} \times \begin{pmatrix}\color{red} B_x \\ \color{green} B_y \\ \color{blue} B_z \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}\color{green} A_y \color{blue}B_z - \color{blue}A_z \color{green}B_y\\ \color{blue} A_z \color{red}B_x - \color{red}A_x \color{blue}B_z\\ \color{red} A_x \color{green}B_y - \color{green}A_y \color{red}B_x \end{pmatrix} A x A y A z × B x B y B z = A y B z − A z B y A z B x − A x B z A x B y − A y B x
相关信息
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols and/or mathematical expressions. Each individual item in a matrix is called an element of the matrix.
一个2行3列的矩阵
[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 ] \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 & 6 \end{bmatrix} [ 1 4 2 5 3 6 ]
通过元素在的矩阵中的位置引用元素 2行3列的矩阵可以称为 2x3 矩阵 相同位置的元素对应相加减
相关信息
A matrix-scalar product multiples each element of the matrix by a scalar.
计算
[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 ] ⋅ [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 ] = [ 1 ∗ 1 + 2 ∗ 3 + 3 ∗ 5 1 ∗ 2 + 2 ∗ 4 + 3 ∗ 6 4 ∗ 1 + 5 ∗ 3 + 6 ∗ 5 4 ∗ 2 + 5 ∗ 4 + 6 ∗ 6 ] \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}1 & \color{red} 2 & \color{red} 3 \\ \color{green}4 & \color{green} 5 & \color{green} 6 \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} \color{blue}1 & \color{purple} 2 \\ \color{blue} 3 & \color{purple} 4 \\ \color{blue} 5 & \color{purple} 6 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}\boxed{ 1*1 + 2*3 + 3*5} & 1*2 + 2*4 + 3*6 \\ 4*1 + 5*3 + 6*5 & 4*2 + 5*4 + 6*6 \end{bmatrix} [ 1 4 2 5 3 6 ] ⋅ 1 3 5 2 4 6 = [ 1 ∗ 1 + 2 ∗ 3 + 3 ∗ 5 4 ∗ 1 + 5 ∗ 3 + 6 ∗ 5 1 ∗ 2 + 2 ∗ 4 + 3 ∗ 6 4 ∗ 2 + 5 ∗ 4 + 6 ∗ 6 ]
两个矩阵相乘要求第一个矩阵的列数和第二个矩阵的行数相同
A ∗ B ≠ B ∗ A A*B \not= B*A A ∗ B = B ∗ A
相关信息
Matrix multiplication is not commutative.
相关信息
A vector is basically a Nx1 matrix where N is the vector's number of components (also known as an N-dimensional vector).
向量可以看作是N行1列的矩阵(反过来矩阵可以看作是NxM的矩阵 可以看作是由M 个Nx1 的向量构成的。
相关信息
The identify matrix is an NxN matrix with only 0s except on its diagonal.
[ 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} \color{red} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \color{red} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \color{red} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & \color{red} 1 \end{bmatrix} 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
相关信息
The identity matrix is usually a starting point of generating other transformation matrices
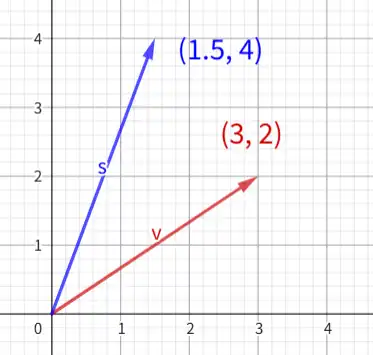
|350x333 将向量 v ⃗ \vec{v} v s ⃗ \vec{s} s
相关信息
If we represent the scaling variables as (S1,S2,S3) we can define a scaling matrix on any vector (x,y,z) as:
[ S 1 0 0 0 0 S 2 0 0 0 0 S 3 0 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ ( x y z 1 ) = ( S 1 ⋅ x S 2 ⋅ y S 3 ⋅ z 1 ) \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}{S_1} & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 \\ \color{green}0 & \color{green}{S_2} & \color{green}0 & \color{green}0 \\ \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}{S_3} & \color{blue}0 \\ \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}1 \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} \color{red}{S_1} \cdot x \\ \color{green}{S_2} \cdot y \\ \color{blue}{S_3} \cdot z \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} S 1 0 0 0 0 S 2 0 0 0 0 S 3 0 0 0 0 1 ⋅ x y z 1 = S 1 ⋅ x S 2 ⋅ y S 3 ⋅ z 1
在单位矩阵的基础上,对角线上第一(n)行的元素对应第一(n)个维度的缩放值
相关信息
Moving the vector based on a translation vector.
[ 1 0 0 T x 0 1 0 T y 0 0 1 T z 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ ( x y z 1 ) = ( x + T x y + T y z + T z 1 ) \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}1 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}{T_x} \\ \color{green}0 & \color{green}1 & \color{green}0 & \color{green}{T_y} \\ \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}1 & \color{blue}{T_z} \\ \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}1 \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} x + \color{red}{T_x} \\ y + \color{green}{T_y} \\ z + \color{blue}{T_z} \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 T x T y T z 1 ⋅ x y z 1 = x + T x y + T y z + T z 1
Tx 表示x方向移动的距离
4维向量中的最后一个分量 w 称为齐次坐标 Homogeneous coordinates ,有了这个分量就可以用矩阵对x,y,z作加减了。
暂略
相关信息
We can combine multiple transformations in a single matrix thanks to matrix-matrix multiplication.
T r a n s . S c a l e = [ 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 0 1 3 0 0 0 1 ] . [ 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 1 ] = [ 2 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 0 0 2 3 0 0 0 1 ] Trans . Scale = \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}1 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}1 \\ \color{green}0 & \color{green}1 & \color{green}0 & \color{green}2 \\ \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}1 & \color{blue}3 \\ \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}1 \end{bmatrix} . \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}2 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 \\ \color{green}0 & \color{green}2 & \color{green}0 & \color{green}0 \\ \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}2 & \color{blue}0 \\ \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}2 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}1 \\ \color{green}0 & \color{green}2 & \color{green}0 & \color{green}2 \\ \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}2 & \color{blue}3 \\ \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}1 \end{bmatrix} T r an s . S c a l e = 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 2 3 1 . 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 1 = 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 2 3 1
先放大后移动
[ 2 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 0 0 2 3 0 0 0 1 ] . [ x y z 1 ] = [ 2 x + 1 2 y + 2 2 z + 3 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}2 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}1 \\ \color{green}0 & \color{green}2 & \color{green}0 & \color{green}2 \\ \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}2 & \color{blue}3 \\ \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}1 \end{bmatrix} . \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}2x + \color{red}1 \\ \color{green}2y + \color{green}2 \\ \color{blue}2z + \color{blue}3 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 2 3 1 . x y z 1 = 2 x + 1 2 y + 2 2 z + 3 1
由于矩阵乘法不满足交换律,所以变换的顺序很重要。后进行的变换会对先进行的变换产生影响。
S c a l e . T r a n s = [ 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 1 ] . [ 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 2 0 0 1 3 0 0 0 1 ] = [ 2 0 0 1 0 2 0 4 0 0 2 6 0 0 0 1 ] Scale . Trans = \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}2 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 \\ \color{green}0 & \color{green}2 & \color{green}0 & \color{green}0 \\ \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}2 & \color{blue}0 \\ \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}1 \end{bmatrix} . \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}1 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}0 & \color{red}1 \\ \color{green}0 & \color{green}1 & \color{green}0 & \color{green}2 \\ \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}0 & \color{blue}1 & \color{blue}3 \\ \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}0 & \color{purple}1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 2 & 0 & 4 \\ 0 & 0 & 2 & 6 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} S c a l e . T r an s = 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 1 . 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 2 3 1 = 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 4 6 1
应用到向量:
[ 2 0 0 1 0 2 0 4 0 0 2 6 0 0 0 1 ] . [ x y z 1 ] = [ 2 x + 1 2 y + 4 2 z + 6 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 2 & 0 & 4 \\ 0 & 0 & 2 & 6 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} . \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \color{red}2x + \color{red}1 \\ \color{green}2y + \color{green}4 \\ \color{blue}2z + \color{blue}6 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 4 6 1 . x y z 1 = 2 x + 1 2 y + 4 2 z + 6 1
可以看到scale的效果应用到了Trans 上
通常变换的顺序为:
相关信息
It is advised to first do scaling operations, then rotations and lastly translations when combining matrices
参考:无伤理解欧拉角中的“万向死锁”现象 - YouTube
指定变换顺序 以及 变换角度后就确定了最终的变换矩阵; 在确定了变换的顺序后,用户调整变换角度值的顺序 对 变换的顺序没有影响;